Welcome to a comprehensive guide on mastering podcast editing using Audacity, a free and powerful audio editing software. This resource provides a step-by-step approach to enhance your podcast production, covering everything from installation and basic editing techniques to advanced mixing and troubleshooting. Whether you’re a seasoned podcaster or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to elevate your podcast to new heights.
From setting up your Audacity workspace to optimizing your final audio export, this guide will walk you through every crucial step. Learn how to effectively trim, adjust volume, remove noise, and apply advanced techniques to create polished and professional-sounding podcasts.
Introduction to Podcast Editing with Audacity
Podcasts have become a ubiquitous form of media consumption, offering listeners a diverse range of content from news and interviews to storytelling and educational discussions. Their popularity stems from the flexibility and accessibility they provide, allowing creators to share their thoughts and insights with a global audience. Creating a compelling podcast involves more than just recording; it necessitates careful planning, recording, and post-production, including audio editing.The process of podcast creation encompasses several crucial stages, beginning with concept development and script writing.
Following this, recording the audio is vital, often requiring multiple takes to capture the desired quality. A crucial subsequent step is the meticulous process of audio editing. This stage involves cleaning up audio, removing unwanted noises, enhancing the overall sound quality, and ensuring a professional listening experience for the audience. High-quality audio editing software plays a critical role in achieving these goals.
Podcast Creation Stages
Creating a podcast requires a systematic approach. The process begins with identifying a niche or topic, crafting compelling content, and developing a consistent schedule. This is followed by the recording phase, which necessitates careful attention to audio quality. The final and essential step is audio editing, ensuring a polished and professional final product.
The Role of Audio Editing Software
Audio editing software, such as Audacity, is indispensable for transforming raw audio recordings into polished podcasts. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for cleaning up audio, removing unwanted noises, and enhancing the overall sound quality. These tools are crucial for achieving a professional listening experience. Sophisticated editing software offers features for adding music, sound effects, and even altering the pace and tone of the audio to enhance the listener’s engagement.
A Concise History of Audacity
Audacity is a free, open-source audio editor that has gained widespread popularity for its ease of use and powerful features. Developed by volunteers, Audacity was initially conceived in 2000, driven by the desire for a comprehensive audio editor that was accessible to everyone. The project quickly gained traction, attracting a dedicated community of users and developers who continue to contribute to its ongoing evolution.
This community-driven approach has resulted in a robust and constantly improving piece of software.
Benefits of Using Audacity for Podcast Editing
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Free | Audacity is entirely free to download and use, eliminating financial barriers for aspiring podcasters. |
| User-Friendly Interface | Audacity boasts a straightforward interface, making it easy for users of all technical skill levels to navigate and utilize its features. |
| Versatile Editing Tools | Audacity offers a wide array of tools for audio manipulation, including noise reduction, equalization, and sound effects integration, catering to a wide range of podcasting needs. |
| Cross-Platform Compatibility | Audacity runs seamlessly on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it accessible to a diverse audience. |
| Extensive Community Support | Audacity has a thriving online community, providing readily available support, tutorials, and troubleshooting assistance to users. |
Setting Up Audacity for Podcast Editing
Audacity is a powerful and free audio editor, making it an excellent choice for podcasting. This section details the essential steps for installing, launching, and preparing Audacity for your podcast editing workflow. We will also cover audio file formats and input/output device setup.Proper setup is crucial for a smooth podcast editing experience. This involves correctly installing and configuring Audacity, importing your audio files, and ensuring compatibility with various audio formats.
Knowing how to set up your audio input/output devices will allow you to record directly into Audacity.
Installing and Launching Audacity
Audacity is readily available for download on the official website. Download the appropriate installer for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux). Follow the on-screen instructions during the installation process. Once installed, launch Audacity from your applications menu.
Importing Audio Files
Audacity allows you to import various audio file types. To import an audio file, click “File” in the menu bar and then “Import.” Select the audio file from your computer and choose the location where you want to place it within Audacity.
Supported Audio Formats
Audacity supports a wide array of audio formats. These formats typically include .wav, .mp3, .aiff, .ogg, and .flac. The specific formats supported may vary slightly depending on your Audacity version.
Setting Up Audio Input/Output Devices
To record audio directly into Audacity, you must set up your audio input and output devices. In Audacity, navigate to “Edit” > “Preferences” > “Devices.” Select the appropriate microphone or other audio input device. Choose your output device for playback.
Audio File Compatibility Table
| File Type | Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| .wav | Excellent | Uncompressed format, high quality, often preferred for editing. |
| .mp3 | Good | Compressed format, good balance of quality and file size, suitable for distribution. |
| .aiff | Excellent | Uncompressed format, high quality, common on macOS. |
| .ogg | Good | Open-source, compressed format, suitable for podcasts. |
| .flac | Excellent | Lossless compressed format, high quality, ideal for preserving original audio. |
| .aac | Good | Compressed format, widely used, suitable for podcast distribution. |
Basic Editing Techniques in Audacity
Mastering basic audio editing techniques in Audacity is crucial for producing high-quality podcasts. These skills allow you to refine recordings, remove unwanted sections, enhance clarity, and ensure a polished listening experience for your audience. Understanding these techniques empowers you to effectively manage your audio files, creating a professional and engaging podcast.
Trimming Unwanted Parts
Efficiently trimming unwanted segments is essential for maintaining a smooth and focused podcast. Audacity offers a straightforward process for precisely cutting and removing extraneous audio. This technique allows for removing pauses, introductory remarks, or any other parts you want to omit from your final product.
- Select the portion of the audio you want to remove.
- Use the “Select” tool to highlight the area you wish to eliminate. Ensure accurate selection by adjusting the selection boundaries if needed.
- Right-click on the selected portion and choose “Delete” from the context menu. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut “Delete” or “Backspace” to delete the selected section.
Using Zoom and Pan Features
Precise audio editing often demands high levels of magnification. The “Zoom” feature in Audacity provides the necessary level of detail for fine-tuning audio edits. The “Pan” feature, on the other hand, allows adjusting the spatial placement of audio elements within the stereo field.
- Zoom in on the waveform to inspect minute details and make adjustments. Zoom controls are typically found within the main Audacity interface.
- Employ the “Pan” feature to manipulate the positioning of audio tracks within the stereo spectrum. Adjust the panning to center, left, or right channels as needed to improve clarity or create a more immersive listening experience. Panning is crucial for creating a more spatial audio effect, useful for sound effects or dialogue.
Adjusting Volume Levels and Gain
Fine-tuning volume levels and gain ensures that all audio segments within the podcast are at optimal levels. This consistency is critical for a balanced and clear listening experience. Adjusting volume is essential for maintaining a consistent listening experience for the audience, preventing jarring changes in volume.
- Select the portion of the audio you want to adjust.
- Use the “Volume” tool within the Audacity interface to increase or decrease the volume of the selected portion. This tool is usually found in the toolbar or effects menu.
- Alternatively, you can use the “Gain” feature to boost or attenuate the overall amplitude of the selected audio segment. This allows for a more precise adjustment of the audio level.
Noise Reduction Techniques
Noise reduction is a valuable technique in podcast editing, especially for recordings captured in noisy environments. Effective noise reduction enhances clarity and improves the overall quality of the podcast. This method minimizes unwanted background sounds without altering the desired audio content.
- Employ the “Noise Reduction” tool to identify and remove unwanted background noises. This tool is typically found in the Effects menu of Audacity.
- Precisely select the audio segment containing the unwanted noise to apply the noise reduction effect. The Audacity interface offers options for defining the noise profile.
- Adjust the noise reduction settings to achieve the desired level of noise reduction. Experiment with different settings to minimize background noise effectively without affecting the audio quality of the main content.
Removing Background Noises
Removing background noises is a critical aspect of podcast editing, crucial for maintaining the clarity and focus of the audio content. A smooth, noise-free audio experience is important for audience engagement and enjoyment. The precise removal of background noise improves the overall listening experience, enhancing the podcast’s professional appeal.
- Use the “Noise Reduction” tool to analyze and isolate the unwanted background noise.
- Employ the “Auto-Noise Reduction” feature in Audacity for automated noise reduction. This feature is effective for general noise reduction tasks.
- Adjust the settings to eliminate background noise while preserving the quality of the podcast content.
Advanced Editing Techniques in Audacity
Mastering Audacity’s advanced features allows for a polished and professional podcast. This section delves into mixing and mastering audio, adding sound effects and music, creating fades and transitions, and implementing echo or reverb effects. These techniques elevate your podcast beyond basic editing, creating a richer listening experience for your audience.Advanced techniques build upon the fundamental editing skills learned previously.
Proficiency in these methods is crucial for crafting high-quality podcasts that stand out from the crowd. By mastering these advanced techniques, you will gain the tools to enhance your podcast’s audio quality and overall presentation.
Audio Mixing and Mastering
Proper mixing and mastering ensure a balanced and loudness-consistent podcast. Audacity’s mixer allows precise adjustments to volume levels, panning (positioning audio in the stereo field), and equalization (adjusting frequencies). Understanding how these parameters affect the overall sound is vital for creating a high-quality listening experience. Mastering aims to create a consistent and professional sound across all episodes, while mixing ensures individual elements work harmoniously.
These processes work together to optimize the audio’s loudness and balance.
Adding Sound Effects and Music
Adding sound effects and music can significantly enhance a podcast’s atmosphere and storytelling. Audacity provides tools for importing and manipulating audio files. Import sound effects and music files into your project. Use the “Import” option to load your audio files. Adjust volume, pitch, and pan to create the desired impact.
The use of appropriate sound effects can enhance specific moments, while well-chosen music can set a mood or underscore transitions. This careful selection of audio elements creates a dynamic listening experience.
Creating Fades and Transitions
Fades and transitions smoothly connect different segments of your podcast. Fades gradually reduce or increase audio volume, creating a seamless transition between segments. Using crossfades, a combination of fades applied to both audio tracks, can blend the end of one clip with the beginning of another. This method avoids abrupt changes in volume and enhances the flow of the podcast.
Transitions, on the other hand, can be complex and involve audio layering, special effects, and audio transitions. Audacity’s “Effect” menu provides various tools for manipulating transitions.
Creating Echo or Reverb Effects
Echo and reverb effects can add depth and dimension to your podcast’s audio. Audacity allows you to create realistic echo or reverb effects. Apply echo and reverb to specific sound elements to enhance their impact or to create a particular ambiance. For example, a reverb effect can be applied to background music to make it sound more spacious.
These effects are useful in creating specific moods and enriching the overall sound.
Comparison of Basic and Advanced Editing Techniques
| Technique | Basic Editing | Advanced Editing |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Editing | Cutting and pasting, basic volume adjustments | Mixing, mastering, using EQ, panning, adding effects |
| Sound Effects | Limited use of basic sound effects | Creative integration of sound effects and music, layering |
| Transitions | Simple cuts | Smooth fades, crossfades, transitions using effects |
| Audio Effects | Basic effects (e.g., normalization) | Complex effects (e.g., echo, reverb, distortion) |
Mastering Audio for Podcasts with Audacity
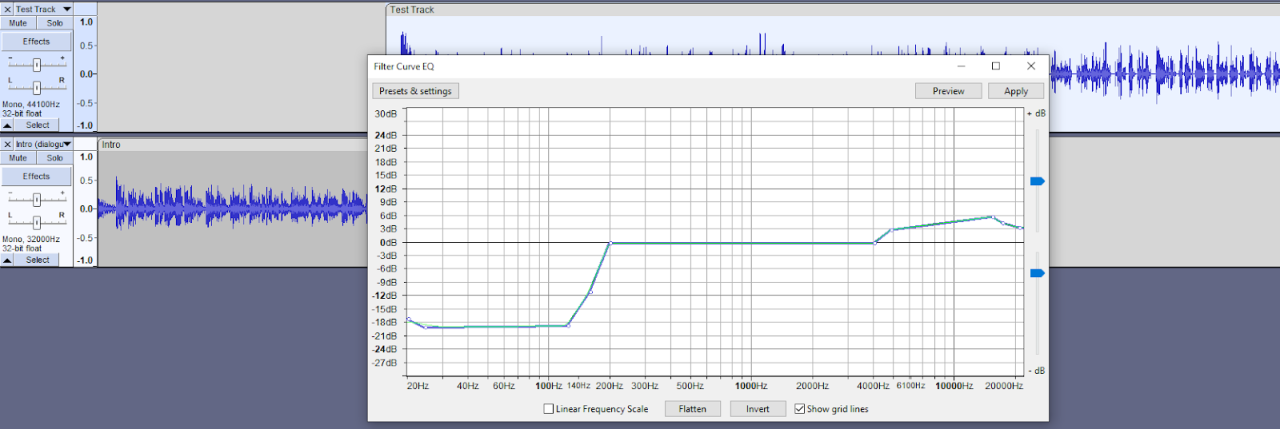
Optimizing audio quality is crucial for creating a professional and engaging podcast. Audacity, while free, provides powerful tools to fine-tune your audio, ensuring your listeners enjoy a clear and consistent listening experience. This section details strategies for enhancing audio quality within Audacity, focusing on key aspects like audio levels, sample rates, bit depths, and export formats.Proper audio levels, sample rates, and bit depths directly influence the clarity, dynamic range, and overall quality of your podcast.
By understanding these parameters, you can leverage Audacity’s features to craft high-quality audio suitable for various podcast platforms.
Optimizing Audio Quality
Audio quality is paramount for a successful podcast. By mastering these techniques, you can significantly improve the overall listening experience.
Proper Audio Levels
Maintaining consistent audio levels is vital for preventing clipping and maintaining a clear listening experience. Clipping occurs when audio signals exceed the maximum recording level, resulting in distortion and a loss of dynamic range. Audacity’s built-in meters help you monitor and adjust audio levels in real-time, ensuring you avoid this problem.
Impact of Sample Rate and Bit Depth
The sample rate and bit depth of your audio files significantly affect the audio quality. Higher sample rates capture more data, leading to a wider frequency range and better sound detail. Bit depth influences the signal-to-noise ratio, impacting the level of background noise and overall clarity. A higher bit depth generally produces cleaner audio.
| Sample Rate (Hz) | Bit Depth (bits) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 44,100 | 16 | Common standard, suitable for most podcasts |
| 48,000 | 24 | Higher fidelity, suitable for professional podcasts |
| 96,000 | 24 | Highest fidelity, ideal for audiophiles and critical listening |
Exporting Audio Files for Podcast Platforms
Exporting your audio files in the correct format is essential for compatibility with podcast platforms. Different platforms may have specific requirements, and failing to meet these can lead to issues with playback and file compatibility.
Common Audio Export Formats
- MP3: A widely used format, offering good compression and compatibility with most devices. However, MP3 compression can lead to a slight loss of audio quality compared to uncompressed formats. It is a suitable format for general distribution.
- WAV: An uncompressed format preserving all audio information. It maintains the highest audio quality but requires larger file sizes, making it less practical for distribution to a wider audience.
- AIFF: Another uncompressed format similar to WAV, suitable for maintaining high audio quality but can also have large file sizes.
- M4A: A compressed format with high quality and excellent compatibility with various devices. It is a good choice for podcasts requiring a balance of quality and file size.
Troubleshooting Common Audacity Issues
Audacity, while a powerful and free audio editor, can occasionally encounter problems. This section addresses common issues and provides practical solutions to ensure smooth podcast editing. Understanding these troubleshooting steps will empower you to efficiently resolve unexpected difficulties.Effective troubleshooting relies on identifying the root cause of the problem. Careful observation of symptoms, like distorted audio or unexpected glitches, is key to pinpoint the underlying issue.
This section will detail various scenarios and provide systematic approaches for resolution.
Identifying Audio File Compatibility Problems
Different audio formats have varying compatibility with Audacity. Understanding these nuances can prevent unexpected issues. Problems may arise when opening files from unsupported formats, or when exporting files to incompatible formats.
- Incorrect File Format: Audacity may not be able to open a file if it is not a supported format. Check if the file extension corresponds to a format that Audacity can handle. Common formats include WAV, AIFF, MP3, and OGG. If you encounter an unsupported format, converting the file to a compatible format using other audio tools may be necessary.
- Corrupted Audio Files: Audio files can become corrupted during transfer or storage. Corrupted files may lead to glitches or errors in Audacity. Try repairing the file using dedicated repair tools or, if that’s not possible, re-record the audio section.
- Incompatible Encoding: The encoding of an audio file can affect compatibility. Audacity may not handle files encoded in specific formats. If a file isn’t opening, explore different encoding options.
Resolving Audio Distortion or Glitches
Distortion or glitches in audio can stem from various sources, including input/output issues or problems within the audio file itself.
- Distorted Audio Input: Issues with your microphone or audio interface may lead to distortion. Ensure your microphone is positioned correctly and try adjusting its gain level within Audacity. If distortion persists, investigate the input device for potential problems.
- Audio File Corruption: As mentioned before, corrupted audio files can result in glitches or distortions during playback or editing. Consider re-recording the affected segment.
- High Input Levels: Over-recording audio can lead to clipping and distortion. Reduce the input level or use a different recording device or settings.
Troubleshooting Input/Output Device Problems
Audio input and output devices are crucial for recording and playback. Issues with these devices can directly impact the quality of your audio.
- Input Device Issues: Audacity may not detect your microphone or other audio input devices. Check your audio settings to ensure the device is selected and configured correctly. Try restarting your computer.
- Output Device Issues: Problems with your output device (speakers or headphones) can manifest as muted audio or distorted sound. Verify the device is correctly connected and configured in your system’s audio settings.
- Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible audio drivers can cause errors. Update your drivers from the manufacturer’s website to ensure compatibility.
Troubleshooting Workflow Table
The following table provides a structured approach to troubleshoot common audio editing problems.
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Distortion | High input levels, faulty equipment, corrupted audio file | Reduce input gain, check equipment, re-record or repair the file |
| Glitches/Artifacts | Corrupted audio file, compatibility issues | Re-record audio, check file format, use a different encoding |
| Audio Not Playing/Recording | Input/output device issues, driver problems, incorrect settings | Check device connections, update drivers, verify Audacity settings, restart computer |
Best Practices for Podcast Editing with Audacity
Maintaining consistent audio quality and meticulous file management are crucial for a professional-sounding podcast. These best practices ensure your listeners have a seamless listening experience, free from jarring inconsistencies. Effective organization also streamlines your workflow, preventing frustration and wasted time as your podcast grows.Following a structured approach to podcast editing with Audacity not only enhances the listening experience but also saves you time and effort in the long run.
By adhering to these best practices, you can create a polished and professional podcast that resonates with your audience.
Consistent Audio Quality
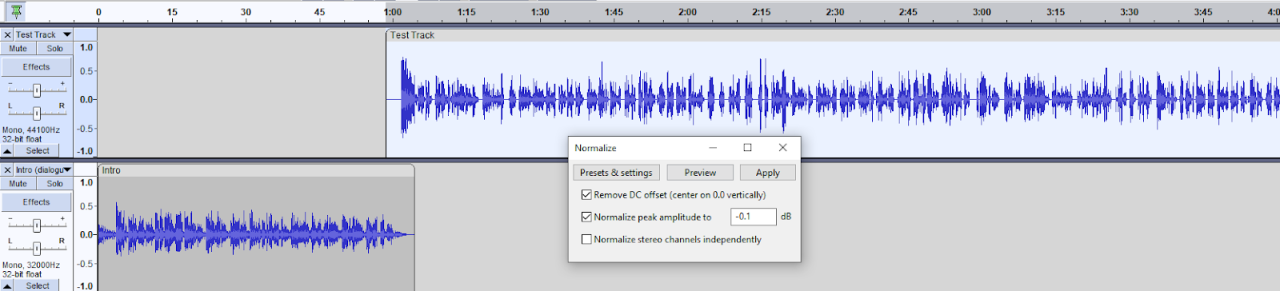
Maintaining consistent audio quality across your podcast episodes is essential for a professional and engaging listening experience. This involves ensuring a similar level of volume, clarity, and sound presence throughout. Variations in audio quality can disrupt the listener’s flow and detract from the overall enjoyment of the podcast. Using consistent audio settings and editing techniques, such as normalization, during the podcast editing process, helps in maintaining the quality.
Proper Naming Conventions for Audio Files
Employing a clear and consistent naming convention for your audio files is critical for efficient organization and easy retrieval. Descriptive filenames make it simple to locate specific audio segments. This also helps in avoiding confusion, particularly as your podcast library grows. For example, instead of simply “episode 1,” use “episode1_interview_with_expert_john_doe.”
Organizing and Managing Audio Files
Effective organization and management of your audio files are paramount to a smooth podcast editing workflow. A well-structured file system ensures that you can easily locate and retrieve any audio clip, whether it’s a sound effect or a portion of a conversation. Employing a logical folder structure, like “episodes,” “sound effects,” and “music,” is recommended. Subfolders within these main categories (e.g., “episodes/episode1/intros”) further enhance the organization.
Creating Backups of Audio Projects
Regularly backing up your audio projects is essential to prevent data loss. Accidental deletion, hardware failures, or software glitches can result in the loss of valuable audio data. Using cloud storage, external hard drives, or a combination of both provides a safety net. This safeguard helps protect your investment in time and effort. A good rule of thumb is to create backups at regular intervals, like daily or weekly.
Essential File Management Best Practices
A structured approach to file management ensures efficient and effective podcast production. These best practices streamline your workflow and minimize the risk of errors:
- Use a consistent naming convention. Use a descriptive format (e.g., “episode1_intro_music.wav”) to easily identify the content of the file.
- Create a hierarchical folder structure. Organize files by episode, sound effects, music, and other categories. This will help locate specific audio clips quickly.
- Create backups regularly. Back up your audio files to external drives or cloud storage services to prevent data loss. Automated backups are preferable for larger projects.
- Label all files clearly. Use relevant metadata (tags, s) to help with future searches.
- Store files in multiple locations. If possible, duplicate files on a separate drive or cloud service to protect against single point of failure.
Practical Examples of Podcast Editing with Audacity
This section provides practical, step-by-step examples of podcast editing using Audacity. These examples illustrate how to enhance your podcast’s professional quality by addressing common editing tasks, from intro and outro adjustments to noise reduction and audio enhancement. Each example demonstrates a workflow, making it easy to apply these techniques to your own podcast projects.These examples will help you visualize the process and gain confidence in using Audacity to create polished podcasts.
Editing a Podcast Intro
A well-crafted intro sets the tone for your podcast. Editing the intro involves refining the audio quality and ensuring a seamless transition to the main content. A common task is trimming silence or unwanted audio at the beginning or end of the intro.
- Import the Intro Audio: Open Audacity and import the audio file containing the podcast intro.
- Select the Intro Segment: Use the selection tool to highlight the section of the audio file that constitutes the actual intro.
- Trim Silence: Employ the “Trim” feature to remove any silence at the beginning or end of the intro.
- Adjust Levels: Use the “Gain” tool to adjust the volume levels of the intro, ensuring it blends seamlessly with the main episode.
- Export the Intro: Export the edited intro as a new file.
Editing a Podcast Outro
The outro is crucial for concluding your podcast and thanking listeners. Editing the outro might involve adding closing remarks, music, or sound effects.
- Import the Outro Audio: Open Audacity and import the audio file containing the podcast outro.
- Add Closing Remarks (if necessary): If the outro requires additional audio, record or import the closing remarks using the Audacity recorder or by importing an external audio file.
- Adjust Volume Levels: Ensure that the volume levels of the outro and the previous segment match for a smooth transition.
- Add Music or Sound Effects (Optional): Add background music or sound effects to create a more polished outro.
- Export the Outro: Export the edited outro as a new file.
Removing Background Noise from an Interview
Background noise is a common issue in interviews, particularly in podcasts recorded in noisy environments. Audacity provides tools for reducing or eliminating these distractions.
- Import the Interview Audio: Open Audacity and import the interview audio file.
- Noise Reduction: Use the “Noise Reduction” tool in Audacity. Select a section of the audio containing only background noise.
- Apply Noise Reduction: Use the “Noise Reduction” tool to reduce or eliminate the background noise.
- Adjust Settings: Adjust the noise reduction settings as needed to achieve the desired result without significantly affecting the quality of the interview.
- Export the Interview: Export the edited interview as a new file.
Adding Music and Sound Effects to a Podcast Episode
Adding music and sound effects enhances the podcast’s engagement and creates a more immersive listening experience. It’s important to select appropriate music and sound effects that align with the podcast’s theme and tone.
- Import Audio and Music: Import the podcast episode and the music/sound effects files into Audacity.
- Place Music/Effects: Use the “Select” and “Move” tools to place the music or sound effects at the desired points in the episode.
- Adjust Volume Levels: Ensure that the volume levels of the music/effects and the podcast audio are balanced.
- Fade Transitions (Optional): Use the “Fade In” and “Fade Out” tools to smoothly transition between different segments of the episode and the music/effects.
- Export the Episode: Export the episode with the added music and sound effects.
Demonstrating a Sample Podcast Editing Workflow
This workflow Artikels a typical podcast editing process using Audacity.
- Import Files: Import the audio files for the episode.
- Intro and Outro Editing: Trim, adjust, and export intro and outro segments.
- Content Editing: Trim unwanted segments and silence.
- Sound Effects and Music: Add sound effects and music to enhance the episode.
- Export the Podcast Episode: Export the final podcast episode file.
Final Wrap-Up
This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed roadmap for utilizing Audacity in your podcast editing journey. By following the steps Artikeld, you’ve gained a solid foundation for creating high-quality podcasts. Remember, consistent practice and exploration of Audacity’s features are key to mastering podcast production. Now, go forth and create captivating podcasts!